Current Carrying Capacity Multi Strand Copper Wire

Mono conductors rubber insulated pvc insulated heat resistant.
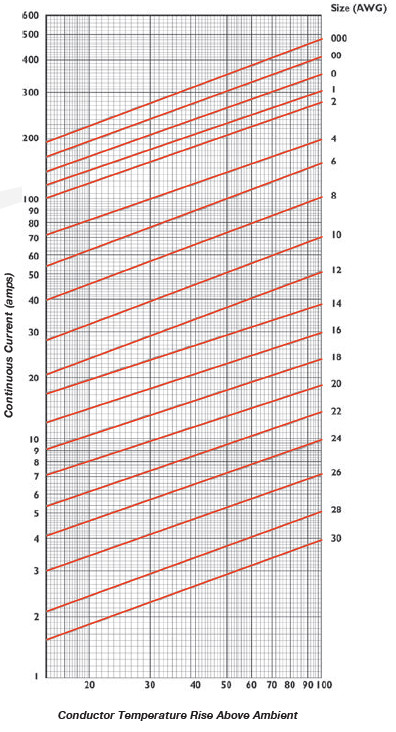
Current carrying capacity multi strand copper wire. A solid wire consists of a solid metal core while stranded wires are made of a quantity of thinner wires that are twisted together into an organized bundle. Heat caused by an electrical current flowing through a conductor will determine the amount of current a wire will handle. Current carrying capacity of copper conductors current carrying capacity is defined as the amperage a conductor can carry before melting either the conductor or the insulation. Awg is sometimes also known as brown and sharpe b s wire gauge.
Because of the small gaps between the strands in a stranded wire a stranded wire with the same current carrying capacity and electrical resistance as a solid wire always have a slightly larger overall diameter. Amp chart lead wire current carrying capacity ampacity awg size insulated conductor temperature rating awg size at 80 c at 90 c at 105 c at 125 c at 150 c at 200 c 40 0 33 0 49 0 55 0 60 0 71 0 78 40 38 0 47 0 68 0 77. On or at surfaces. Heat caused by an electrical current flowing through a conductor will determine the amount of current a wire will handle.
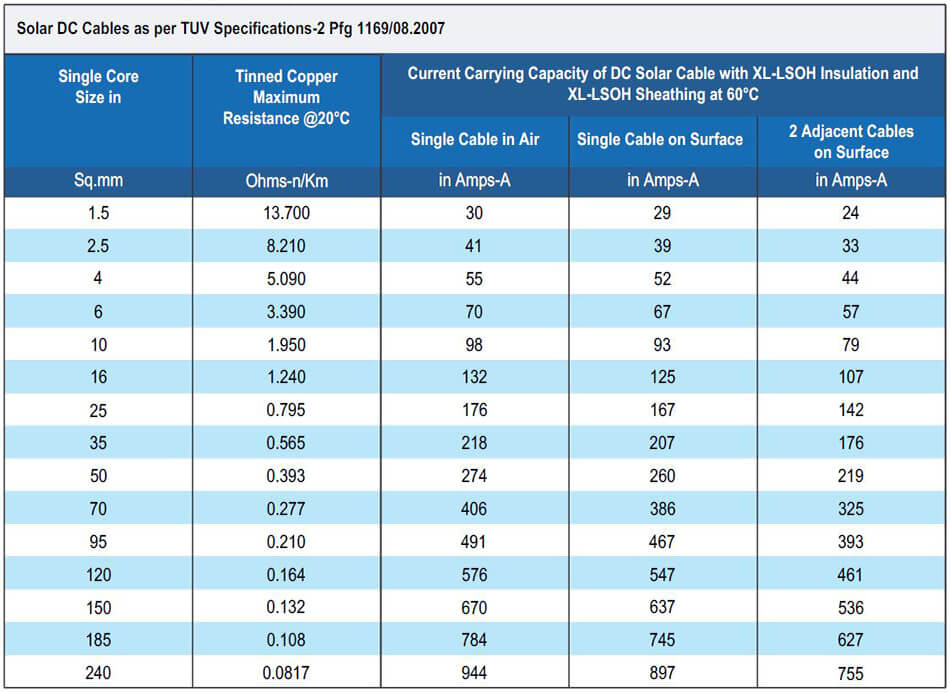
The awg table below is for a single solid round conductor. The stranded wire consists of many strands and has air gaps among the wires. 8 impedance and skin effect. 1 current ratings for up to 1000 v pvc insulated single and multicore wiring cables ambient temperature up to 30 o c values for resistance are based on electrical resistivity for copper 1 724 x 10 8 ω m 0 0174 μω m and electrical resistivity for aluminum 2 65 x 10 8 ω m 0 0265 μω m.
Current carrying capacity cables with a nominal voltage up to 1000 v and heat resistant cables vde 0298 t4 08 03 table 11 column 2 and 5. Current carrying capacity of copper conductors. In careful engineering the voltage drop insulation temperature limit thickness thermal conductivity and. Multi conductor cables except for house or handheld units rubber.
It significantly decreases the surface area where dissipation can take place. So the surface area is larger. Current carrying capacity is defined as the amperage a conductor can carry before melting either the conductor or the insulation. The higher the gauge number the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire.
But the solid wire uses only one strand. The following chart is a guideline of ampacity or copper wire current carrying capacity following the handbook of electronic tables and formulas for american wire gauge.